-Practice Quizizz for Fall 2024 Semester Final
Click here to practice the quizizz.
https://quizizz.com/join?gc=82454113
 Klein Prep Computer Science
Klein Prep Computer Science
-Practice Quizizz for Fall 2024 Semester Final
Click here to practice the quizizz.
https://quizizz.com/join?gc=82454113

Due Date: May 6, 2024
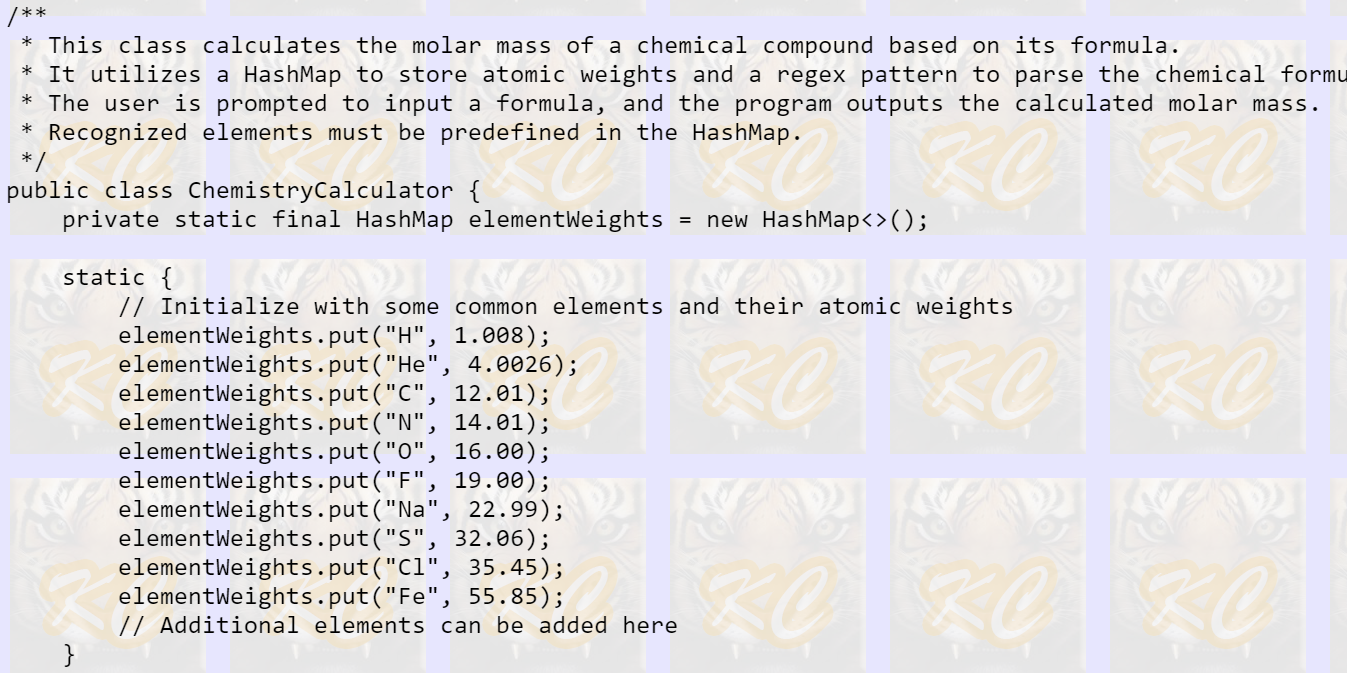
Java program to calculate Molar Mass
How to Calculate Molar Mass of a Chemical Compound
To calculate the molar mass of a chemical compound:
1. Identify the Formula: Note the compound's molecular formula, e.g., H2O.
2. Get Atomic Masses: Use a periodic table to find
the mass of each element in grams per mole (g/mol).
3. Count Atoms: Count how many atoms of
each element are in the formula.
4. Calculate: Multiply each element's
atomic mass by its count, then sum these values.
For instance, water (H2O) has a molar mass
of 18.016 g/mol, calculated as (2 x 1.008) + 16.00.
To learn more about calculating Molar Mass click here.
Your files will be:
PX_MolarMass_lastname.java (Actual Java program)
PX_MolarMass_lastname.png (Screen shot of the
program in the Eclipse IDE)
PX_MolarMass_lastname.mp4 (Video)
(Video should include an explanation of the program
and showing it running successfully)
Be sure to drop these files into google classroom.
Click here to read the specs for this program.
Click here to read the Pseudocode for this program.
Click here to learn about HashMap with examples.
(You will use the HashMap in this assignments.)
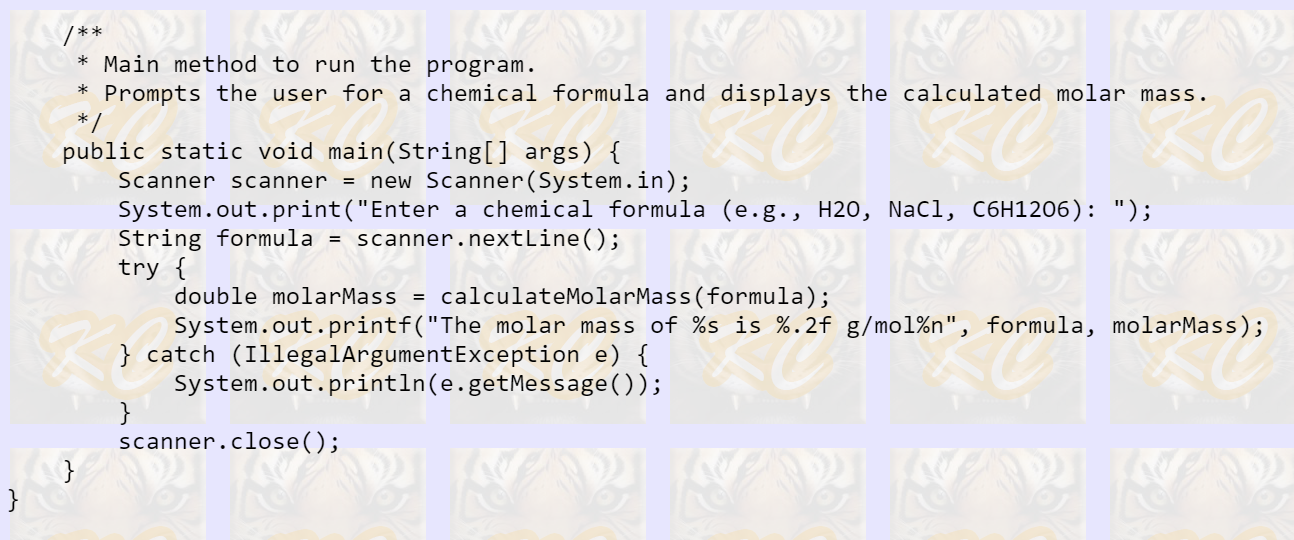
I have the program code below with a section of code missing.
**** Section 1 *****
 **** Section 2 *****
**** Section 2 *****
 **** Section 3 *****
**** Section 3 *****
 **** Section 4 *****
**** Section 4 *****
Due Date: May 8, 2024
Snake Game
Snake game in Java involves setting up a
basic GUI and game logic.
Below is a simple implementation
using the javax.swing
package for the GUI components.
This version of the game includes basic
controls and mechanics to move
the snake around the
board and eat food items to
grow in length.
This program is one of the longer
one you have done.
To assist you, you may want to
comment out sections
of the code as you test it.
Your files will be:
PX_Snake_lastname.java (Actual Java program)
PX_Snake_lastname.png (Screen shot of the
program in the Eclipse IDE)
PX_Snake_lastname.mp4 (Video)
(Video should include an explanation of the program
and showing it running successfully)
(If you do not fully understand the code,
use the comments and google the java commands.)
Be sure to drop these files into google classroom.
Use Eclipse and code the program below.
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.KeyAdapter;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Random;
public class SnakeGame extends JPanel implements ActionListener {
// Constants for the game dimensions and speed
private final int WIDTH = 300;
private final int HEIGHT = 300;
private final int DOT_SIZE = 10;
private final int ALL_DOTS = 900;
private final int RANDOM_POSITION = 29;
private final int DELAY = 140;
// Arrays to hold the coordinates of the snake's joints
private final int x[] = new int[ALL_DOTS];
private final int y[] = new int[ALL_DOTS];
private int dots; // current size of the snake
private int apple_x; // x coordinate of the apple
private int apple_y; // y coordinate of the apple
private boolean leftDirection = false;
private boolean rightDirection = true;
private boolean upDirection = false;
private boolean downDirection = false;
private boolean inGame = true;
private Timer timer;
private Random random;
public SnakeGame() {
initBoard();
}
private void initBoard() {
addKeyListener(new TAdapter());
setBackground(Color.black);
setFocusable(true);
setPreferredSize(new Dimension(WIDTH, HEIGHT));
loadGame();
}
private void loadGame() {
dots = 3;
for (int z = 0; z < dots; z++) {
x[z] = 50 - z * 10;
y[z] = 50;
}
locateApple();
// We use a timer to call actionPerfomed method at fixed delays
timer = new Timer(DELAY, this);
timer.start();
}
public void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
super.paintComponent(g);
doDrawing(g);
}
private void doDrawing(Graphics g) {
if (inGame) {
g.setColor(Color.red);
g.fillOval(apple_x, apple_y, DOT_SIZE, DOT_SIZE);
for (int z = 0; z < dots; z++) {
if (z == 0) {
g.setColor(Color.green);
g.fillRect(x[z], y[z], DOT_SIZE, DOT_SIZE);
} else {
g.setColor(Color.green.darker());
g.fillRect(x[z], y[z], DOT_SIZE, DOT_SIZE);
}
}
Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().sync();
} else {
gameOver(g);
}
}
private void gameOver(Graphics g) {
String msg = "Game Over";
Font small = new Font("Helvetica", Font.BOLD, 14);
FontMetrics metr = getFontMetrics(small);
g.setColor(Color.white);
g.setFont(small);
g.drawString(msg, (WIDTH - metr.stringWidth(msg)) / 2, HEIGHT / 2);
}
private void checkApple() {
if ((x[0] == apple_x) && (y[0] == apple_y)) {
dots++;
locateApple();
}
}
private void move() {
for (int z = dots; z > 0; z--) {
x[z] = x[(z - 1)];
y[z] = y[(z - 1)];
}
if (leftDirection) {
x[0] -= DOT_SIZE;
}
if (rightDirection) {
x[0] += DOT_SIZE;
}
if (upDirection) {
y[0] -= DOT_SIZE;
}
if (downDirection) {
y[0] += DOT_SIZE;
}
}
private void checkCollision() {
for (int z = dots; z > 0; z--) {
if ((z > 4) && (x[0] == x[z]) && (y[0] == y[z])) {
inGame = false;
}
}
if (y[0] >= HEIGHT) {
inGame = false;
}
if (y[0] > 0) {
inGame = false;
}
if (x[0] >= WIDTH) {
inGame = false;
}
if (x[0] < 0) {
inGame = false;
}
if (!inGame) {
timer.stop();
}
}
private void locateApple() {
int r = (int) (Math.random() * RANDOM_POSITION);
apple_x = ((r * DOT_SIZE));
r = (int) (Math.random() * RANDOM_POSITION);
apple_y = ((r * DOT_SIZE));
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (inGame) {
checkApple();
checkCollision();
move();
}
repaint();
}
private class TAdapter extends KeyAdapter {
@Override
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) {
int key = e.getKeyCode();
if ((key == KeyEvent.VK_LEFT) && (!rightDirection)) {
leftDirection = true;
upDirection = false;
downDirection = false;
}
if ((key == KeyEvent.VK_RIGHT) && (!leftDirection)) {
rightDirection = true;
upDirection = false;
downDirection = false;
}
if ((key == KeyEvent.VK_UP) && (!downDirection)) {
upDirection = true;
rightDirection = false;
leftDirection = false;
}
if ((key == KeyEvent.VK_DOWN) && (!upDirection)) {
downDirection = true;
rightDirection = false;
leftDirection = false;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Snake Game");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.add(new SnakeGame());
frame.pack();
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
Due Date: May 14, 2024
Complete the following assignment
Projectile Motion
Projectile motion is a form of motion
experienced by an object or particle that is
thrown near the Earth's surface and
moves along a curved path
under the action of gravity only.
This type of motion is characterized
by the horizontal motion having
constant velocity, while the vertical
motion is subjected to
uniform acceleration due to gravity.
The main aspects of projectile motion can be
determined by the initial velocity of the projectile,
the angle of projection,
and the acceleration due to gravity.
The trajectory of a projectile is a parabolic path,
and key metrics include the range
(the horizontal distance traveled),
the maximum height reached,
and the time of flight.
Understanding projectile motion
is crucial in various applications
such as sports, ballistics, and physics education.
Your files will be:
PX_Projectile_lastname.java (Actual Java program)
PX_Projectile_lastname.png (Screen shot of the
program in the Eclipse IDE)
PX_Projectile_lastname.mp4 (Video)
(Video should include an explanation of the program
and showing it running successfully)
(If you do not fully understand the code,
use the comments and google the java commands.)
Be sure to drop these files into google classroom.
Use Eclipse and code the program below.
I have the program code below with a section of code missing.



-Locate your Cyber Range Passwords below by seat number.
Sign on ids for Period 3
Click here and get your id and password.
Sign on ids for Period 4
Click here and get your id and password.
Click here for your cyber range.
https://apps.cyber.org/login
-Using Linux and the python interpreter
If you have forgotten how to boot up your Kali Linux machine and run python.
Click here for full instructions.
KP Java Programming – Course Outline
Section 1 - Getting Started
Java Basics
Data Types
Arrays and References
Operators and Constructs
Java Objects
Dynamic Memory Allocation
Java Methods
Java Strings
Section 2 - Classes and Objects
Class Design
Fields and Access Control
Constructors
Method Overloading
Static Methods
Inheritance
Method Overriding
Using
final
and
super
Abstract Classes and Methods
Dynamic Binding
Polymorphism
Section 3 - Working with Classes
Using
instanceof
Interfaces
Exception Handling
Exception Objects
throw points, throws clause
try, catch, finally
Section 4 - User Interfaces
Window Applications
Layout Managers
Event Handlers and Listeners
Anonymous Classes and Lambdas
Java Swing APIs
Basic GUI Controls
Menus and MenuBars
Section 5 - Generics and Collections
Why Use Generics?
Generic Classes and Interfaces
Generic Iterators
Collections
ArrayList, LinkedList, HashMap
Section 6 - Threads
Thread States
Extending the
Thread
class
Timer Thread
Implementing the
Runnable
interface
Section 7 - File I/O
Input and Output Streams
Binary and Text Files
Files and Directory Methods
Appendix
Java Language
JavaFX