Drop off the following file into google classroom.
Your file name will be PX_States_lastname.py
Your file name will be PX_States_lastname.mp4 (Video of the program running)
Your file name will be PX_States_lastname.png (Screen print of the program inside the IDE or jdoodle)
file:///C/Users/JoePhotos/Downloads/CapitalStates.txt[1/31/2024 10:42:23 PM] comment remove
MIN = 0
MAX = 49
import random
def main():
stateDict = {'Alabama': 'Montgomery',
'Alaska': 'Juneau',
'Arizona': 'Phoenix',
'Arkansas': 'Little Rock',
'California': 'Sacramento',
'Colorado': 'Denver',
'Connecticut': 'Hartford',
'Delaware': 'Dover',
'Florida': 'Tallahassee',
'Georgia': 'Atlanta',
'Hawaii': 'Honolulu',
'Idaho': 'Boise',
'Illinois': 'Springfield',
'Indiana': 'Indianapolis',
'Iowa': 'Des Moines',
'Kansas': 'Topeka',
'Kentucky': 'Frankfort',
'Louisiana': 'Baton Rouge',
'Maine': 'Augusta',
'Maryland': 'Annapolis',
'Massachusetts': 'Boston',
'Michigan': 'Lansing',
'Minnesota': 'Saint Paul',
'Mississippi': 'Jackson',
'Missouri': 'Jefferson City',
'Montana': 'Helena',
'Nebraska': 'Lincoln',
'Nevada': 'Carson City',
'New Hampshire': 'Concord',
'New Jersey': 'Trenton',
'New Mexico': 'Santa Fe',
'New York': 'Albany',
'North Carolina': 'Raleigh',
'North Dakota': 'Bismarck',
'Ohio': 'Columbus',
'Oklahoma': 'Oklahoma City',
'Oregon': 'Salem',
'Pennsylvania': 'Harrisburg',
'Rhode Island': 'Providence',
'South Carolina': 'Columbia',
'South Dakota': 'Pierre',
'Tennessee': 'Nashville',
'Texas': 'Austin',
'Utah': 'Salt Lake City',
'Vermont': 'Montpelier',
'Virginia': 'Richmond',
file:///C/Users/JoePhotos/Downloads/CapitalStates.txt[1/31/2024 10:42:23 PM] comments remove
'Washington': 'Olympia',
'West Virginia': 'Charleston',
'Wisconsin': 'Madison',
'Wyoming': 'Cheyenne'}
statesList = list(stateDict)
correct = 0
incorrect = 0
again = 'y'
while (again == 'y'):
num = random.randint(MIN,MAX)
state = statesList[num]
print('\n' + state)
ans = input("\nEnter the capital of this state: ")
if (ans == stateDict[state]):
correct += 1
print("Correct")
again = input("Type y to play again, anything else to stop: ")
else:
incorrect += 1
print("Incorrect")
again = input("Type y to play again, anything else to stop: ")
print("\nYou have",correct,"correct answers")
print("\nYou have",incorrect,"incorrect answers")
main()
Due Date: January 30, 2024
Big Idea 3
ALGORITHMS AND PROGRAMMING
Watch these video below:
You need to watch the entire video from start to finish.
 3.6Conditionals
3.6: Daily Video 1 In this video, we will create algorithms using selection to choose from possible outcomes. We can select which statements to execute based on the outcome of a condition.
3.6: Daily Video 2 In this video, we will implement conditional statements, or “if-statements,” to choose between different blocks of code based on the outcome of a Boolean expression.
3.6: Daily Video 3 In this video, we will determine the outcome of program code that uses conditional statements. We will explore how “if” and “if-else” statements can be used to choose which statements to execute.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
3.6Conditionals
3.6: Daily Video 1 In this video, we will create algorithms using selection to choose from possible outcomes. We can select which statements to execute based on the outcome of a condition.
3.6: Daily Video 2 In this video, we will implement conditional statements, or “if-statements,” to choose between different blocks of code based on the outcome of a Boolean expression.
3.6: Daily Video 3 In this video, we will determine the outcome of program code that uses conditional statements. We will explore how “if” and “if-else” statements can be used to choose which statements to execute.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
 3.7NestedConditionals
3.7: Daily Video 1 In this video, we will determine the outcome of program code that uses nested conditional statements. When conditionals are nested, we select statements based on the outcome of multiple conditions.
3.7: Daily Video 2 In this video, we will create algorithms that use nested conditional statements. When nesting conditional statements, we must adjust the logic and flow to meet the needs of our algorithm.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
3.7NestedConditionals
3.7: Daily Video 1 In this video, we will determine the outcome of program code that uses nested conditional statements. When conditionals are nested, we select statements based on the outcome of multiple conditions.
3.7: Daily Video 2 In this video, we will create algorithms that use nested conditional statements. When nesting conditional statements, we must adjust the logic and flow to meet the needs of our algorithm.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
 3.8Iteration
3.8: Daily Video 1 In this video, we will represent algorithms using iteration with a flow chart or natural language. We can iterate (or repeat) a part of our algorithm as many times as needed to accomplish our goal.
3.8: Daily Video 2 In this video, we will determine the outcome of program code that uses iteration. We will determine how many times to iterate based on the pseudocode provided.
3.8: Daily Video 3 In this video, we will create algorithms that use iteration using pseudocode. Small adjustments in the pseudocode can have a major impact on the outcome of the iteration.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
3.8Iteration
3.8: Daily Video 1 In this video, we will represent algorithms using iteration with a flow chart or natural language. We can iterate (or repeat) a part of our algorithm as many times as needed to accomplish our goal.
3.8: Daily Video 2 In this video, we will determine the outcome of program code that uses iteration. We will determine how many times to iterate based on the pseudocode provided.
3.8: Daily Video 3 In this video, we will create algorithms that use iteration using pseudocode. Small adjustments in the pseudocode can have a major impact on the outcome of the iteration.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
 3.9DevelopingAlgorithms
3.9: Daily Video 1 In this video, we will determine the outcome of similar algorithms. We will compare the similar algorithms to better understand their outcomes.
3.9: Daily Video 2 In this video, we will represent algorithms using a flowchart or natural language. Whether algorithms contain selection or iteration, they must be sequenced properly.
3.9: Daily Video 3 In this video, we will create algorithms by modifying existing correct algorithms. We will explore advantages and concerns that arise when modifying existing correct algorithms.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
3.9DevelopingAlgorithms
3.9: Daily Video 1 In this video, we will determine the outcome of similar algorithms. We will compare the similar algorithms to better understand their outcomes.
3.9: Daily Video 2 In this video, we will represent algorithms using a flowchart or natural language. Whether algorithms contain selection or iteration, they must be sequenced properly.
3.9: Daily Video 3 In this video, we will create algorithms by modifying existing correct algorithms. We will explore advantages and concerns that arise when modifying existing correct algorithms.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
 3.10 Lists
3.10: Daily Video 1 In this video, we will use the pseudocode for lists on the exam reference sheet to implement an algorithm.
3.10: Daily Video 2 In this video, we will use the pseudocode for lists on the exam reference sheet to determine lines of code necessary to complete the algorithm.
3.10: Daily Video 3 In this video, we will use the pseudocode for lists on the exam reference sheet to interpret code to determine the output of given code.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
3.10 Lists
3.10: Daily Video 1 In this video, we will use the pseudocode for lists on the exam reference sheet to implement an algorithm.
3.10: Daily Video 2 In this video, we will use the pseudocode for lists on the exam reference sheet to determine lines of code necessary to complete the algorithm.
3.10: Daily Video 3 In this video, we will use the pseudocode for lists on the exam reference sheet to interpret code to determine the output of given code.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
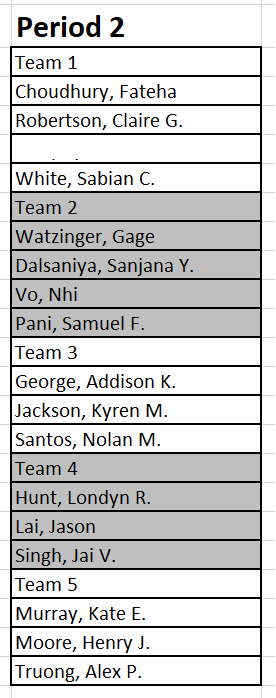 Period 6 Teams
Period 6 Teams
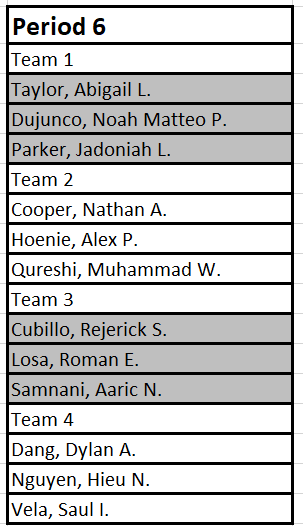

 Period 6 Teams
Period 6 Teams

 3.6Conditionals
3.6: Daily Video 1 In this video, we will create algorithms using selection to choose from possible outcomes. We can select which statements to execute based on the outcome of a condition.
3.6: Daily Video 2 In this video, we will implement conditional statements, or “if-statements,” to choose between different blocks of code based on the outcome of a Boolean expression.
3.6: Daily Video 3 In this video, we will determine the outcome of program code that uses conditional statements. We will explore how “if” and “if-else” statements can be used to choose which statements to execute.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
3.6Conditionals
3.6: Daily Video 1 In this video, we will create algorithms using selection to choose from possible outcomes. We can select which statements to execute based on the outcome of a condition.
3.6: Daily Video 2 In this video, we will implement conditional statements, or “if-statements,” to choose between different blocks of code based on the outcome of a Boolean expression.
3.6: Daily Video 3 In this video, we will determine the outcome of program code that uses conditional statements. We will explore how “if” and “if-else” statements can be used to choose which statements to execute.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
 3.7NestedConditionals
3.7: Daily Video 1 In this video, we will determine the outcome of program code that uses nested conditional statements. When conditionals are nested, we select statements based on the outcome of multiple conditions.
3.7: Daily Video 2 In this video, we will create algorithms that use nested conditional statements. When nesting conditional statements, we must adjust the logic and flow to meet the needs of our algorithm.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
3.7NestedConditionals
3.7: Daily Video 1 In this video, we will determine the outcome of program code that uses nested conditional statements. When conditionals are nested, we select statements based on the outcome of multiple conditions.
3.7: Daily Video 2 In this video, we will create algorithms that use nested conditional statements. When nesting conditional statements, we must adjust the logic and flow to meet the needs of our algorithm.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
 3.8Iteration
3.8: Daily Video 1 In this video, we will represent algorithms using iteration with a flow chart or natural language. We can iterate (or repeat) a part of our algorithm as many times as needed to accomplish our goal.
3.8: Daily Video 2 In this video, we will determine the outcome of program code that uses iteration. We will determine how many times to iterate based on the pseudocode provided.
3.8: Daily Video 3 In this video, we will create algorithms that use iteration using pseudocode. Small adjustments in the pseudocode can have a major impact on the outcome of the iteration.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
3.8Iteration
3.8: Daily Video 1 In this video, we will represent algorithms using iteration with a flow chart or natural language. We can iterate (or repeat) a part of our algorithm as many times as needed to accomplish our goal.
3.8: Daily Video 2 In this video, we will determine the outcome of program code that uses iteration. We will determine how many times to iterate based on the pseudocode provided.
3.8: Daily Video 3 In this video, we will create algorithms that use iteration using pseudocode. Small adjustments in the pseudocode can have a major impact on the outcome of the iteration.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
 3.9DevelopingAlgorithms
3.9: Daily Video 1 In this video, we will determine the outcome of similar algorithms. We will compare the similar algorithms to better understand their outcomes.
3.9: Daily Video 2 In this video, we will represent algorithms using a flowchart or natural language. Whether algorithms contain selection or iteration, they must be sequenced properly.
3.9: Daily Video 3 In this video, we will create algorithms by modifying existing correct algorithms. We will explore advantages and concerns that arise when modifying existing correct algorithms.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
3.9DevelopingAlgorithms
3.9: Daily Video 1 In this video, we will determine the outcome of similar algorithms. We will compare the similar algorithms to better understand their outcomes.
3.9: Daily Video 2 In this video, we will represent algorithms using a flowchart or natural language. Whether algorithms contain selection or iteration, they must be sequenced properly.
3.9: Daily Video 3 In this video, we will create algorithms by modifying existing correct algorithms. We will explore advantages and concerns that arise when modifying existing correct algorithms.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
 3.10 Lists
3.10: Daily Video 1 In this video, we will use the pseudocode for lists on the exam reference sheet to implement an algorithm.
3.10: Daily Video 2 In this video, we will use the pseudocode for lists on the exam reference sheet to determine lines of code necessary to complete the algorithm.
3.10: Daily Video 3 In this video, we will use the pseudocode for lists on the exam reference sheet to interpret code to determine the output of given code.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
3.10 Lists
3.10: Daily Video 1 In this video, we will use the pseudocode for lists on the exam reference sheet to implement an algorithm.
3.10: Daily Video 2 In this video, we will use the pseudocode for lists on the exam reference sheet to determine lines of code necessary to complete the algorithm.
3.10: Daily Video 3 In this video, we will use the pseudocode for lists on the exam reference sheet to interpret code to determine the output of given code.
-----------------------------------------------------------------